Communication in Organisation
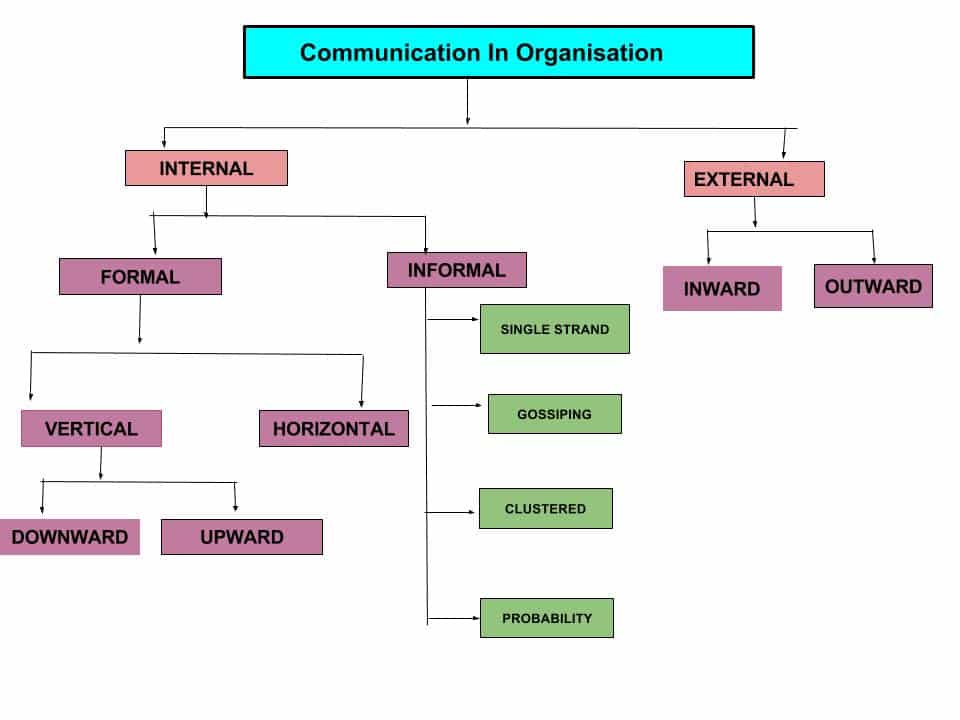
A.Internal Communication
There is a large volume of communication within the organization. The flow of communication within an organization forms a complicated pattern. The volume & the direction are usually determined by the pattern of the hierarchy the level of authority & also by the requirements of tasks.
1. Formal Channels-
Formal channels are those which carry the official messages of the organization. The efficiency of an organization depends on the regular flow of messages. The flow of messages needs to be organized into a well-ordered network to ensure that communication flows easily & reaches the persons who need the information. If communication bypasses the channels someone who needs the information may not get it. These can lead to gaps in information & it may fail to take the required action.
The information has to go through proper channels for eg Clerks from one department are not supposed to exchange official papers directly with clerks from another department, the papers must move through the supervisors or section heads
Formal communication is again subdivided into two types
- Vertical communication
This includes all the messages that move between subordinates & their supervisors. Messages sent from superiors to subordinates are downward communication .messages sent from subordinates to superiors are upward communication. Vertical communication is classified into two types
a ) Downward Communication:-
Messages going from the higher authority levels to the lower level may be written, or oral. Written messages are notes, circulars, notices, and emails. Oral messages may be face-to-face or by telecom or telephone .announcement over the public address system
The common purpose of downward communication is as follows
- Instruction about a specific task
- Information about the practices& Procedures followed by an organization
- The information creates an understanding of the task in relation to other tasks of the organization
- Feedback about subordinates’ performance
- Information about the ideology & the goals of the organization would help them to develop a sense of belonging to the organization
Downward communication must be simple & carefully explained persons at the lower level of the hierarchy may not have sufficient knowledge or understanding of the organization’s work hence they need explanation. Long circulars, written in an official & legal style are not easy to follow. Instruction sheets & employee manuals should be written in a simple style.
A great deal of information is lost as messages move downward. When a message is passed from a senior to a subordinate down the line of command in a chain, It passes through many levels of authority. There is a delay in the movement of the message also the message gets changed and modified & there is a distortion of the message & simplifies it for the understanding & needs of the understanding & needs of the person who is to receive it. If the chain of communication is very long there may be much change &distortion in the message.
Messages which go from subordinates to supervisors & to higher levels of authority are upward communication. These may be written or oral. Written messages are in the form of reports, letters, presentations, notes & email messages. Oral messages may be face to face or by intercom or telephone
The common purposes of upward communication are
- Give information to the management
- Enable the management to learn & understand the concerns of the subordinates
- To enable all the employees to contribute ideas & make suggestions
Open & free upward communication also helps to maintain good staff relations. Employees work better when managers listen to their ideas. Persons at any level in an organization may have good ideas & suggestions for the improvement of the organization. These ideas are encouraged when the organization has good upward communication channels.
- Horizontal or Lateral Channel
Messages that flow between persons of equal status or the same level of authority in the organization are called horizontal or lateral communication. A large amount of communication flows laterally in an organization.
Horizontal communication can be oral or written. Written communication may be in form of letters, memoranda, notes, or reports. copies of the document, oral communication may be in the form of face-to-face talk, intercom, meetings, committee work or conferences
Horizontal communication is needed for several purposes in an organization. It includes both information & persuasion & even for discussion, plans, solving problems, resolving conflicts, negotiation & coordination of work .it serves an important function of providing emotional & social support to one another
B)Informal Channels /Grapevine Communication
In addition to the imposed organizational arrangement, members of groups that work together construct their own communication networks. These informal networks have two basic purposes
- They compensate for inadequacies in the formal network by establishing new links that bypass obstacles that come up in the formal structure. In many groups, there is someone who can expedite the matter at hand often the expeditor is not the person holding official responsibility for locating the right person.
- They serve the needs of the individuals involved these needs may or may not be the same as the goals of the organization. These informal networks link persons with similar interests & experiences & those who simply like one other
The informal network serves a valuable organizational function they protect the individual from becoming isolated from professional colleagues by stimulating him/her to more creative thinking & by supplying a psychological support group. Quite often an informal work relationship completely obscures the formal organizational structure.
The following are types of informal communication
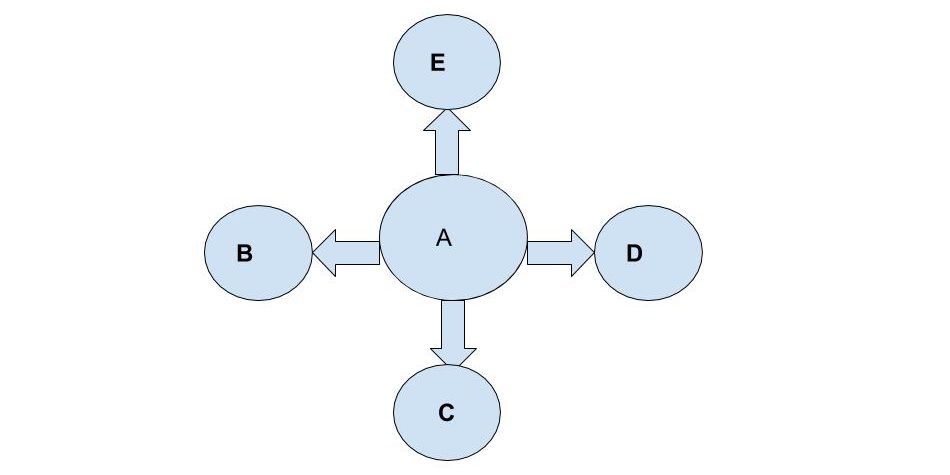
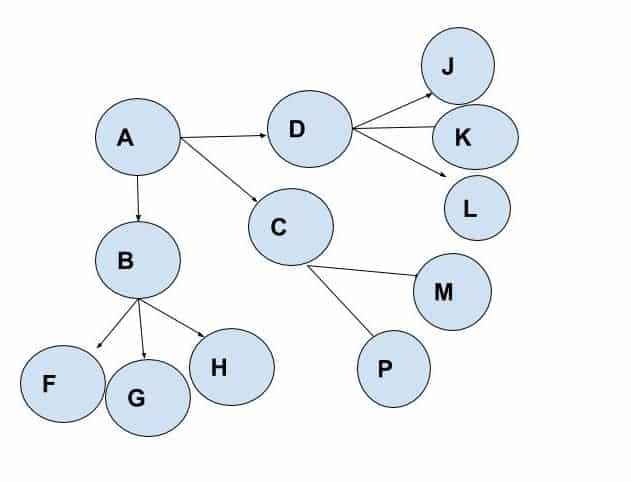
1 Single Strand Chain: The single-strand chain involves the passing of information through a line of persons to the recipient. For Eg, person A tells B, who tells C, who tells D, and so on, till the information has reached most of the persons involved or concerned.
3. Probability Chain: The probability chain is a random process in which someone transmits the information to others and then these to others in a similar way. This chain may also be called a random process.
4 Cluster Chain: In the cluster chain, a person tells the information to the selected persons who may in turn relay (pass) the information to other selected persons. Most of the information communication follows this chain.
B. External Communication
In the organization, there will be a continuous flow of communication. There will be continuous communication with the surroundings outside the organization i.e with Customers, Suppliers, Bankers, etc. An organization has office procedures & system for handling external communication, both the incoming & the outgoing messages are recorded & filled. External communication is divided into the following two types
1 Outward
Messages are sent out to organization customers, suppliers, banks, insurance companies, government departments, the mass media & general public they may be in the form of letters, faxes, telephone calls telegrams, reports advertisement, press handouts speeches visit & so on. The style format & tone of companies’ outgoing communication affect goodwill & public relations. Therefore most organizations have a policy about the style & appearance of the companies’ messages that go out. Copies of outgaining written documents are filed for reference.
2 Inward
An organization receives letters, telegrams, fax, telex messages, reports, brochure circulars, journal magazines, telephonic calls, and personal visits these may be formed customers, suppliers, other organization government departments & so on. These inward communication messages are filed for a record for reference. A written note or summary of visits meetings and telephonic talks may also be filled.