Plant Layout and its affecting factors.
When a new plant is built the main question raises about where to place different types of machinery at different places like the location of stores, inspection cabins, tool rooms maintenance wings, heat treatment other handling equipment. The efficiency of production flow depends largely on how well the various machine production facilities and employee facilities are located in a plant.
According to James Lundy, “Layout identically involves the allocation of space and the arrangement of equipment in such a manner that overall operating costs are minimized”.
According to Mallick and Gandreau, “Plant layout is a floor plan for determining and arranging the designed machinery and equipment of a plant, whether established or contemplated, in the best place, to permit the quickest flow of material, at the lowest cost and with the minimum handling in processing the product, from the receipt of raw material to the shipment of the finished product.
Objectives of good layout
- Provide sufficient production capacity.
- Reduce the cost of material handling.
- Utilization of labor efficiently.
- To reduce accidents.
- It helps to utilize available space efficiently & effectively.
- It provides ease of supervision.
- Facilitates co-9rdination and proper communication.
- Provide better employee safety & health.
- Maintenance can be done in an effective way.
- It improves productivity.
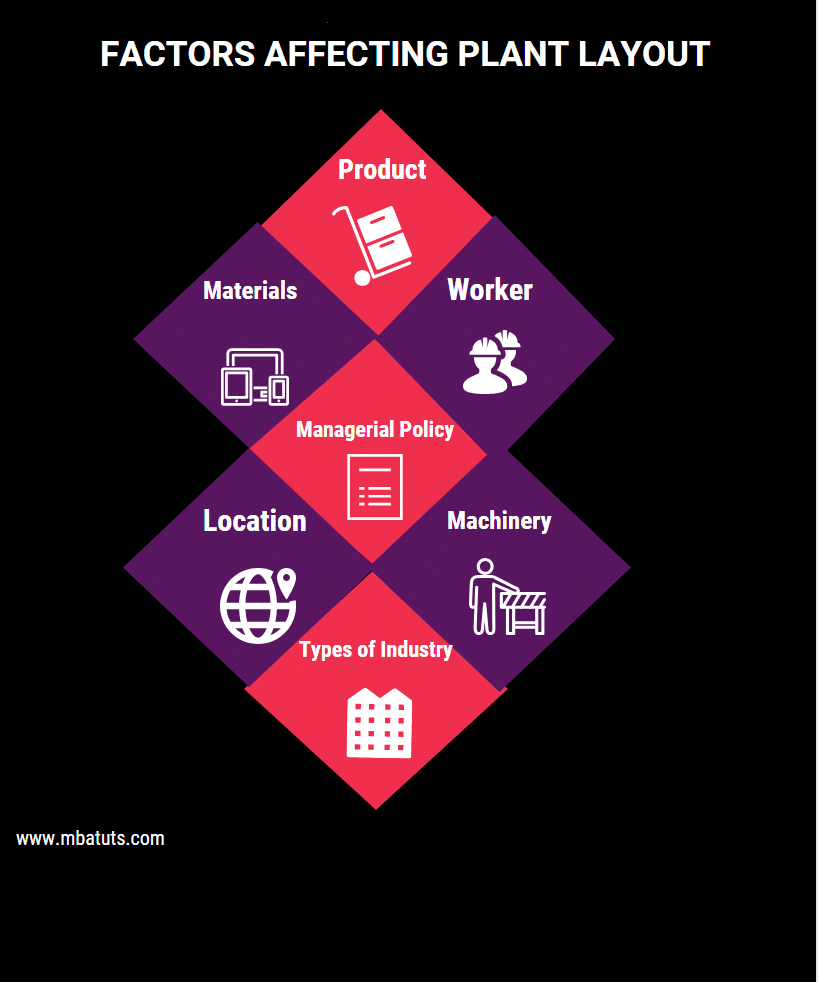
Factors affecting plant layout
1. Material
Every factory needs to buy raw materials in an economic store and they are moved through production centers efficiently for manual or mechanical operations different aspects like the type of material, and size of storage material equipment depend upon.
- The type of raw material used like solid-liquid light or heavy
- The availability or scarcity of material due to seasonal variations.
2. Product
In most cases, the product moves from one workstation to another workstation. In some cases like locomotives and shipbuilding, the is stable but men and machinery are moved to the product.
3. Worker
The position of employees whether remaining stable or moving also influences the layout. Employee facilities like health, locker rooms, and public facilities influence the layout significantly.
4. Machinery
The type of production volume of its production, the type of process & management policy determine the size and type of machinery being installed.
5. Type of industry
Industries in this context may be broadly classified into four types.
i)Extractive industries
It involves the separation of one element from another
ii) Conditioning Industries
Involves changes in form or physical properties.
iii) Analytical industries
It converts raw materials into various elements or constituent parts
iv) Assembly Industries
It involves the production of a product through the use of various elements.
6. Location
a)The soil &size of the site determines the layout.
b) The location of the plant determines the mode of transportation depending on the distance from a source of raw material and market.
7. Managerial Policies
- The volume of production and provision for expansion.
- The extent of automation.
- I am making or buying a particular component.
- Purchasing policy etc.
Following is a video lecture on Plant Layout and its Affecting Factors